
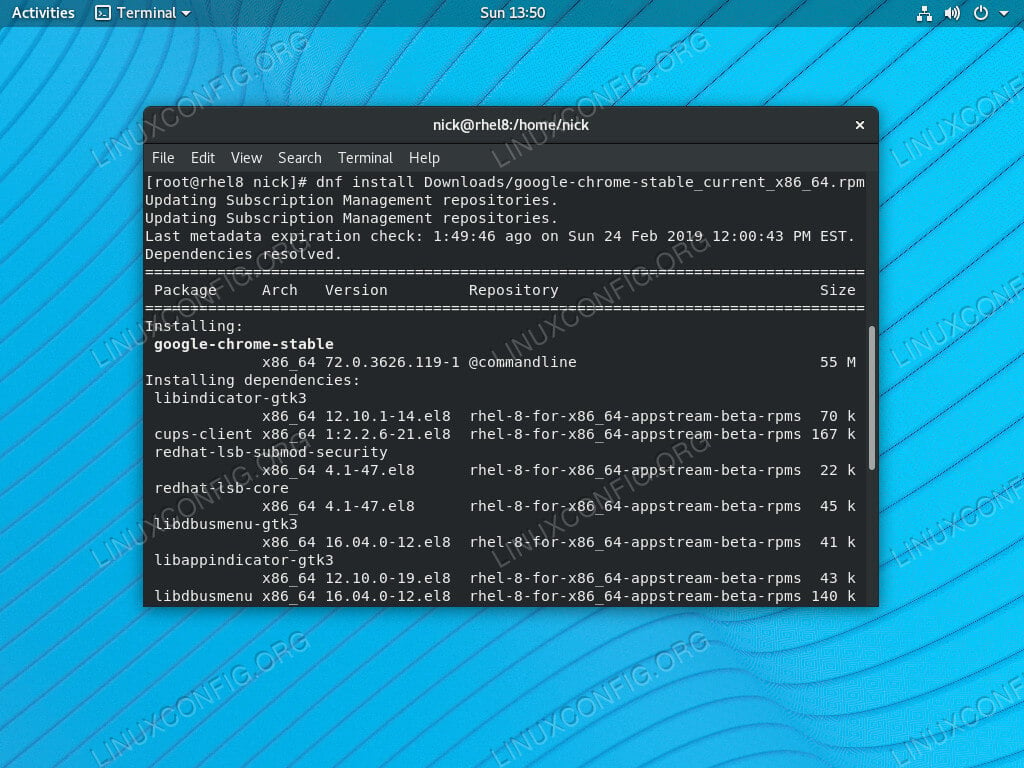
$ git commit -m "My first LinuxShellTips Repo" Your file commits should be associated with a message so that you know exactly what you did to that file when you later revise the project repository. If you have many files inside your repo directory and you want to add them all, use the command: $ git add. Next, let us create a random file with some text: $ sudo nano linuxshelltips.txtĪdd this file to git. The above command tells Git to start tracking all changes inside the linuxshelltips_repo directory when you are adding or removing something. It is through commits that we are able to execute repository changes whether we want to revert a change or proceed with new changes.Ĭreate a directory on your local machine that will be holding your projects. Since a repository holds all your project files and directories, making changes to these files and directories is through commits. $ git config -listĬheck Github Account in Linux Setting up Git Repositories in Linux We can re-check or confirm the configurations we made with this git command. $ git config -global user.email "Your GitHub Email" Create Github Accountįor first time use, you will need the username and email of your GitHub account to configure a global variable that will inform the GitHub cloud service that it is you making changes to your project repo each time you need to upload a file, remove a file, or update a file.įrom your Linux terminal, do the following: $ git config -global user.name "Your GitHub Username" Create a GitHub AccountĬreate a GitHub account if you do not have one. Now that you have the Git version control system installed, you need access to a cloud service like GitHub or GitLab for hosting the various Git repositories you will be creating, updating, and tracking.įor this Guide, let us go with GitHub. With local repositories, project files reside on a local machine or server whereas, with remote repositories, project files reside on a remote machine or server. A repository or repo can be local or remote. $ sudo zypper install git-all Īs mentioned earlier, Git uses a repository as its base storage location. Depending on the Linux operating distribution you are using, you can easily install the Git version control package by referencing either of the following installation commands: $ sudo apt-get install git-all

The wide footprint of Git makes it a compatible candidate for all Linux operating system distributions. With Git, a repository acts as the base storage location for your first project file uploads and will keep track of every change that will affect those files with inclusion to other file uploads that may follow.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
